Notice that the proton closest to the carbonyl group is at a higher chemical shift than the proton in cyclohexene 6 05 ppm for cyclohexenone vs.
Vinylic proton nmr shift.
2002 4 2249 2252 supporting information.
Splitting between vinylic protons in alkenes depends strongly on the geometrical relation ship of the coupled protons.
This is not surprising since the proton is not only vinylic but it is also alpha to a carbonyl group.
Chemical shift d type of proton examples chemical shift in ppm comments.
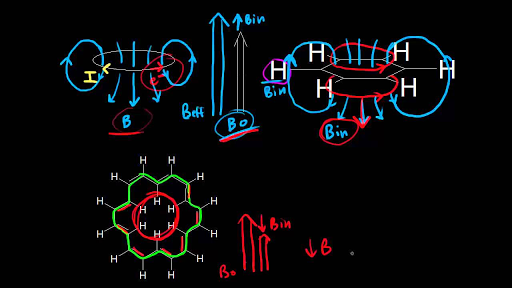
Characteristic proton chemical shiftstype of protonstructurechemical shift ppmcyclopropanec3h60 2primaryr ch30 9secondaryr2 ch21 3tertiaryr3 c h1 5vinylicc c h4 6 5 9acetylenictriple.
Electronegative groups move to the down field left.
0 8 1 5 ppm alkane c h.
This is a general trend add approximately 0 2 0 4 ppm for each additional alkyl group.
Electronegative groups move to the down field left.
Nmr chemical shift values table in the previous post we talked about the principles behind the chemical shift addressing questions like how the ppm values are calculated why they are independent of the magnetic field strength and what is the benefit of using a more powerful instrument.
Table of characteristic proton nmr shifts type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm rch 3 1 aliphatic 0 9 r 2 ch 2 2 aliphatic 1 3 r 3 ch 3 aliphatic 1 5 c c h vinylic 4 6 5 9 c c h vinylic conjugated 5 5 7 5 c c h acetylenic 2 3 ar h aromatic 6 8 5 ar c h benzylic 2 2 3 c c ch 3 allylic 1 7 hc f.
We know that a proton alpha to a carbonyl group is pulled downfield.
Type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm rc h 3 1 aliphatic 0 9 r 2 c h 2 2 aliphatic 1 3 r 3 c h 3 aliphatic 1 5 c c h vinylic 4 6 5 9 c c h vinylic conjugated 5 5 7 5 c.
The proton nmr chemical shift is affect by nearness to electronegative atoms o n halogen and unsaturated groups c c c o aromatic.
The proton nmr chemical shift is affect by nearness to electronegative atoms o n halogen and unsaturated groups c c c o aromatic.
Table of characteristic proton nmr chemical shifts.
The greater the substitution on the carbon bearing the hydrogen the further downfield higher frequency the resonance occurs.
Meo2c ch c nme2 co2me has a chemical shift of 4 49 for the vinylic proton in cdcl3.
However this particular orientation makes such a large contribution that it dominates the chemical shift.